
Except for the years 2003, 2005, 2008, 20, an overall downward trend has been observed since 2000, where household expenditure peaked at 55.3% of GDP.

This was a significant decrease compared with 2019, when it amounted to 52.4 % of GDP. In 2020, EU total household expenditure amounted to 50.5 % of GDP.
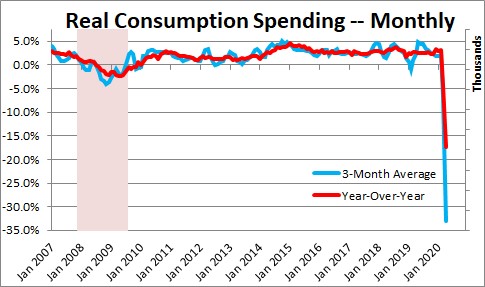
While the figures for 2020 are impacted by the exceptional effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, the evolution of the EU household expenditure between 20 provides insights into longer term trends. The remaining household spending was distributed over 'Health' (4.6 % of total or 2.3 % of GDP), 'Alcoholic beverages, tobacco and narcotics' (4.4 % of total or 2.2 % of GDP), 'Clothing and footwear' (4.1 % of total or 2.1 % of GDP),'Communications' (2.6 % of total or 1.3 % of GDP) and 'Education' (0.9 % of total or 0.5 % of GDP) – which together represented 22.6 % of total expenditure or 11.4 % of EU GDP in 2020. 'Recreation and culture' (7.8 % of total or 4.0 % of GDP) and 'Restaurants and hotels' and 'Furnishings, household equipment and routine household maintenance' (both 6.0 % of total or 3.0 % of GDP) followed. Household expenditure by consumption purpose - COICOP, EU, 2020, share of total Different impacts were observed for ’Health’, where expenditures decreased by 4.7 % in 2020 and increased in 2009 by 0.4% as well as ‘Food and non-alcoholic beverages’ (+3.2 % in 2020 and -1.2 % in 2009).įigure 4. On the other hand, increases were observed in ’Communications’ both in 2020 (by 2.4 %) and 2009 (by 2.1 %), as well as in ’Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels’ (by 1.0 % and by 0.3 % respectively). While consumption categories were mostly affected in the same direction, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was much more severe in areas affected by government lockdowns. However, certain categories showed an increase, notably ’Food and non-alcoholic beverages’ (3.2 %), ’Communications’ (2.4 %) and ’Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels’ (0.3 %).įigure 2: Household consumption expenditure by Member State, % change over the previous year, 2020Ĭomparison with effects of the 2008-2009 financial crisisįigure 3 shows a comparison of changes in household consumption expenditure during the COVID-19 pandemic with the developments during the 2008-2009 financial crisis.

The largest decreases were observed for ’Restaurants and hotels’ (of 37.8 %), ’Clothing and footwear’ (17.3 %), ’Transport’ (of 16.8 %) and ’Recreation and culture’ (16.7 %). To better understand the magnitude of the recent reductions in the household consumption expenditure, Figure 1 shows that certain categories of household consumption expenditure changed unprecedentedly in comparison to 2019. This section presents the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the European aggregates, differences across countries and a comparison with the 2008-2009 financial crisis.

There was a huge impact on both the overall amount and the composition of household consumption even though the majority of Member States put in place government schemes to support enterprises and households in the year 2020. Social distancing measures as well as government restrictions imposed on the movement of people and non-essential economic activities severely affected households' consumption expenditures. The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe had severe economic impacts that are reflected in national accounts estimates for 2020. COVID-19 pandemic impacts on data in 2020


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
